The new memory technologies provide double the bandwidth and density of DDR4.
As the Internet of Things evolves and millions of internet-connected devices get deployed, data center operators are working hard to keep up with the movement of data. They must find ways to meet ever-increasing data and storage needs, while ensuring the quality of service and keeping costs down. For many data center operators, minimizing power consumption is one of their top priorities to reduce operating expenses. Double Data Rate 5 memory, officially abbreviated as DDR5, looks to provide the performance enhancements and power management required in the data center to support 400GE networking speeds.
The new Jedec DDR5 will offer improved performance with greater power efficiency compared to previous-generation DRAM technologies. As planned, DDR5 will provide double the bandwidth and density over DDR4, along with delivering improved channel efficiency. These enhancements, combined with a more user-friendly interface for server and client platforms, will enable high performance and improved power management in a wide variety of applications.
Major manufacturers will soon release their first DDR5 memory modules, bringing increased bandwidth and lower power draw to the table. The new modules will bring in a new generation of high-speed memory that will replace existing standards.
Key Design Considerations
With the improved performance and greater power efficiency of DDR5 versus DDR4 technology, the need for compact, robust DIMM sockets to support this new technology becomes more important. More compact than their DDR4 predecessors, DDR5 DIMM sockets have reduced overall dimensions and heights, along with anti-buckling features for smooth module insertion and crowned contacts that prevent contact-stubbing.
DDR5 provides double the bandwidth and density over DDR4. This means DDR5 DIMM sockets deliver 6.4Gbps speed with lower seating plane for greater PCB and vertical space savings. The pin counts for both DDR4 and DDR5 are the same. Both DIMMS have 288 pins. Also, the pitch is the same for both DDR4 and DDR5. Besides the speed increase, there are some differences in the overall dimensions and the module card thickness. The dimensions of the DDR5 socket connectors are shorter than those for DDR4. For modular card thickness, DDR4 is 1.40+/-0.1mm, while DDR5 is 1.27+/-0.1mm. For the seating plane, it will be reduced from 2.4mm max. on DDR4 to 2.0mm max. on DDR5.
When it comes time to move to DDR5, designers should keep several key considerations in mind specific to socket connectors. DDR5 sockets are keyed to prevent insertion of DDR4 modules, and DDR4 modules cannot work in DDR5 and vice versa.
DDR5 does have higher speed requirements. For SMT terminations, there may be process challenges, and SMT packages perhaps will be more difficult to process compared to through-hole or press-fit terminations. CTE mismatch with the PCB could cause dynamic warpage of the connector.
When using automatic module insertion, it becomes more critical to have a robust DDR5 connector. Some sockets have metal at the latch tower to improve mechanical strength.
DDR5 will have heavier module cards, and the module weight may potentially increase to 65g from 50g. Hence, good and mechanical retention of the connector to the PCB needs to be considered.
Moving to DDR5 Sockets
When moving ahead with DDR5, consider a connector with anti-stubbing contacts that enable robust mating contact and electrical reliability. A halogen-free, high-temperature nylon housing can support high reflow temperatures, while providing environmental sustainability. A vibration and shock-resistant solder tab offers performance and robust PCB retention during rugged operations. Additionally, a metal insert on the socket can support rigorous latch operations, while strengthening the latch tower. A robust, ergonomically designed latch can improve rip-out force and vibration resistance during latching and release of module card. To solve for crushed pins, seek a well-designed terminal and housing.
For other DDR5 considerations, dynamic warpage is a possible concern. In terms of processing, SMT terminations will be more challenging and difficult compared to TH terminations. The assembly process must be properly controlled, and the design and housing material selection are very important. An optimized molding process can reduce internal stress built up inside the housing.
As speeds in the data center increase, DDR5 will be ideal in supporting those speed increases. DDR5 socket production is growing and will continue to grow in the next year.

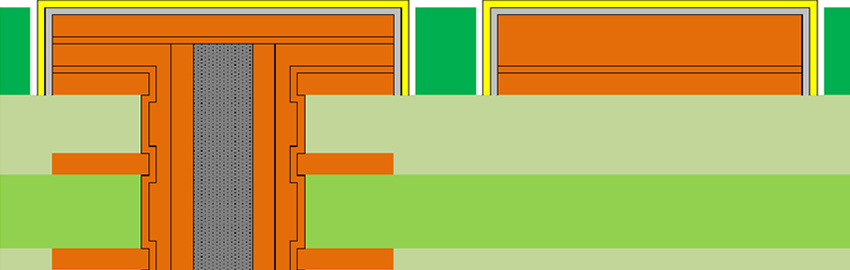
Figure 1. Jedec-recommended PCB footprint options for a DDR5 DIMM 0.85mm pitch 288-pin SMT socket.1
Reference
1. Jedec, “DDR5 DIMM SMT 288 Pin Socket Outline 0.85 MM Pitch Skt,” July 2019.
Wai Kiong Poon is product manager at Molex (molex.com).